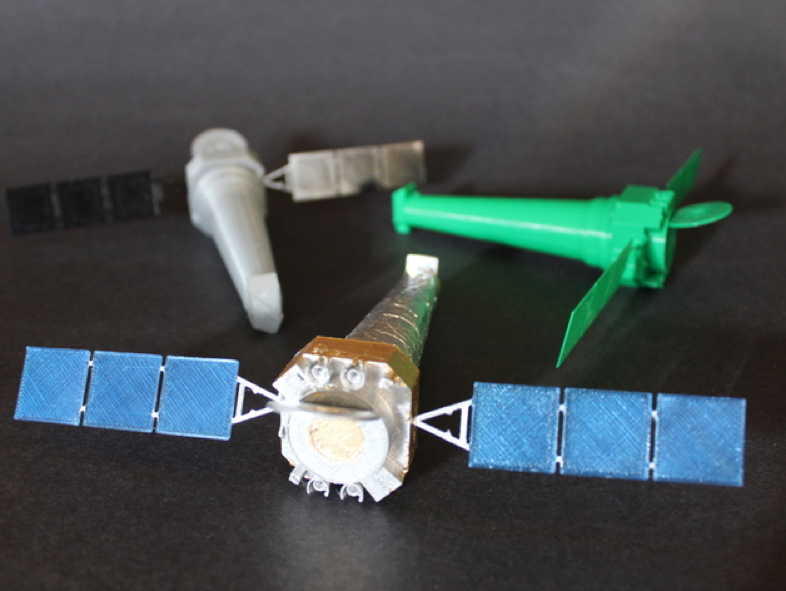
Build Your Own Chandra
Since its launch on July 23, 1999, the Chandra X-ray Observatory has been NASA's flagship mission for X-ray astronomy, taking its place in the fleet of "Great Observatories."
NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory is a telescope specially designed to detect X-ray emission from very hot regions of the Universe such as exploded stars, clusters of galaxies, and matter around black holes. Because X-rays are absorbed by Earth's atmosphere, Chandra must orbit above it, up to an altitude of 139,000 km (86,500 mi) in space. The Smithsonian's Astrophysical Observatory in Cambridge, MA, hosts the Chandra X-ray Center which operates the satellite, processes the data, and distributes it to scientists around the world for analysis. The Center maintains an extensive public web site about the science results and an education program.
Chandra carries four very sensitive mirrors nested inside each other. The energetic X-rays strike the insides of the hollow shells and are focused onto electronic detectors at the end of the 9.2- m (30-ft.) optical bench. Depending on which detector is used, very detailed images or spectra of the cosmic source can be made and analyzed.
3D Printing
- Download the 3D files (Five STL files, 267KB)
- Read the brief instructions below
- Select the 3D printer of your choice.
This example (shown below) was printed at 0.1mm layer height, 8% infill, 2 perimeters. Take a piece of 3mm filament (or dowel) about 6mm long and glue into the centering holes. Align the parts as shown in the photos on thingiverse.com.

To make your 3D printed model more photorealistic you can spray the craft with silver metallic spray paint and/or apply aluminum or thin craft store foil before assembling. Gold paint or ready gold leaf from a local craft store or online store can be added if desired. Rubber cement works well to attach materials to the body of the spacecraft. For the solar panels, you can apply a blue or black glaze or paint. Quick tip: attach the solar panels last.
Disclaimer: The Chandra X-ray Center does not endorse any commercial product.
DOWNLOADABLES
How To Hold a Dead Star in Your Hand
3D Printing Handouts
Learn how to print your own 3D Chandra
3D files (Five STL files, 267KB)
LINKS TO OTHER ACTIVITIES
Coding & Astronomy
Recoloring the Universe with Pencil Code
3D Printing
Universe in 3D
Astronomy
Make the Most of Your Universe
Learn more at chandra.si.edu/corps/